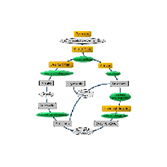
Cells are the fundamental units of biological structure and function, serving as the primary sites for metabolism. Metabolic assays are essential tools for detecting metabolite levels and measuring activity in metabolic reactions and cellular processes. These assays provide critical insights into cellular metabolic pathways and phenotypic changes, making them indispensable for research in areas like cancer and metabolic diseases.Elabscience® offers a comprehensive portfolio of metabolism assay kits. These kits cover key areas including oxidative stress, glycolysis, lipid metabolism, ferroptosis, cuproptosis, and mitochondrial function analysis.Designed for versatility, the kits are compatible with a wide range of sample types and work seamlessly with common laboratory instruments. This includes spectrophotometers, standard microplate readers, fluorescence microplate readers, and flow cytometers.
- 96T
- 48T
- 96T
- 48T
- 96T
- 48T




