Abstract: Oxidative stress, the pathological condition with the imbanlance of oxidation and antioxidation, has been proved to make contribution to the accurance and development of multiple kinds of diseases. This paper mainly refers to recent researches in diabetes, ischemia-reperfusion injury, indiopathic oligospermia, nuerodegenerative diseases, cancer treatment and so on. Biomarkers of oxidative stress had been widely used in the evaluations of related diseases judgement and drug treatment, which shows the importance of oxidative stress evaluation in disease research and drug development.
The following sections will be discussed in this article,
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Introduction of Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress is the imbanlanced situation between oxidation and antioxidation in some abnormal conditons. During this situation, the produced free redical is too much to be eliminated by the antioxidant system of body, that will end up with the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS), and leads to oxidatice damage[1]。
Oxidative stress is clesely related to many kinds of diseases, especially some of the senile and chronic diseases including diabetes mellitus[2], cardiovascular diseases[3], inflammatory and immune diseases[4], hypertension[5], ischemia-reperfusion injury[6], neurodegenerative diseases[7] and so on.。
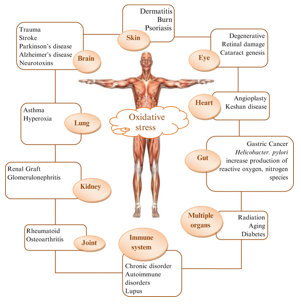
Figure 1. Diseases that proved to be related to oxidative stress[8]
Oxidative stress could be evaluated through the changing of oxidants, antioxidants or oxidation products as the increasing of oxidant capability and decreasing of antioxidant capability could be observed.
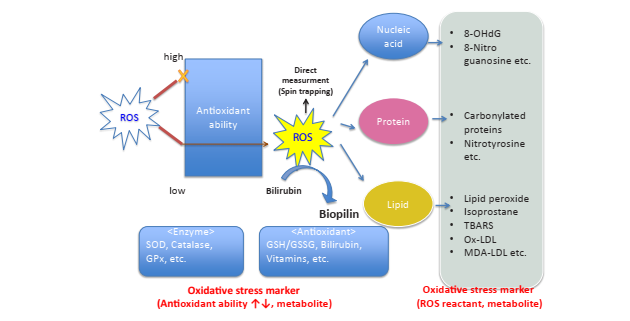
Figure 2. Biomarkers for oxidative stress evaluation[9]
The relationship between oxidative stress and mechanism of diseases and their potential treatment could be investigated through direct or indirect measurement of oxidative stress biomarkers that can be mainly devided in three types: ROS, antioxidant and oxidation products.
Oxidative Stress Evaluation in Diseases
Research
1. Diabetes research
① The machenism of diabetes induced by oxidative stress
Diabetes is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia, which is mainly caused by impaired insulin secretion or physiological effects. Insulin deficiency induced by islet B cell apoptosis causing by excess ROS will end up with hyperglycemia, which will lead to complications with chronic damage and dysfunction of nerves, heart, blood vessels, liver, kidney, eyes et al.
② The application of oxidative stress biomarkers in diabetes research
Oxidative stress evaluation was mainly been applied in the researches of accurence machenism and treatment effet of complications with diabetes. Mimiranpour[10] found that electron beam irradiation can relieve oxidative stress and assist in the treatment of diabetes symptoms by evaluating hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), malondialdehyde (MDA), Glutathione reductase (GR), et al. Alagal[2] figured out the protective function of Fesitin for cardiomyocyte protection in type I diabetes rat by reducing ROS and MDA. Ogunlabi[11] and Akinnuga[12] investigated the palliative and therapeutic effects of natural prodicts in diabetes and liver complication by combining the evaluation of oxidative stress biomarkeres like superoxide dismutase (SOD) and MDA together with liver function biomarkers such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alkaline phosphatase (ALP). The supression effect of drugs and natural product in diabetic nephropathy thearapy was investigated by Periandavan[13], Mebuza[14] and Akinnuga[15] using oxidative stress biomarkeres with kidney function biomarkers like urea (BUN), uric acid (UA) and creatinine.
In addition, decreasing of SOD, catalase (CAT) and reduced glutathion (GSH) can be observed in both arsenic[16] and bisphenol A[17] reduced diabetes. The risk of diabetes-induced rentinopathy could be induced with SOD and glutathion peroxidase (GPx) activity decreasing and MDA increasing[18], while the risk could be reduced by essential oil from Fructus Alpiniae zerumbet[19]. The relationship between diabetes and high fat diet[20] induced cardiovascular[21], nervous[22] and inflammatory[23] diseases were also been investigated.
Table 1. Application of oxidative stress biomarkers in diabetes researches
|
Sample |
Intervention |
Rising indicator |
Dropping indicator |
Reference |
|
Mouse blood |
Electron beam |
GR |
H2O2,MDA |
[10] |
|
Rat heart |
Fesitin |
SOD,GSH |
ROS,MDA |
[3] |
|
Rat liver |
Bredemolic Acid |
SOD,GPx |
MDA |
[12] |
|
Rat kidney |
diimine ruthenium (II) (II) |
SOD,GPx |
MDA |
[14] |
|
Bredemolic Acid |
SOD,GPx |
MDA |
[15] |
2. Ischemia-reperfusion
Ischemia-reperfusion (I-R) injury obtains quite complex mechanism, it is one of the important factors affecting the success rate of cardiopulmonary bypass, cardiopulmonary cerebral resuscitation, limb replantation, organ transplantation and so on. I-R injury is now beliened to be related to oxidative damage, calcium overloading and inflammatory response causing by neutrophils, in which the production of large amount of oxidative free redicals played an important role during the process[24].The free redicals produced by I-R consumed the endougenous antioxidants rapidly, destroyed the structure and function of endothelial cells, leaded to tissue edema, bleeding and exudation. It also destoryed the non cellular structure and function of intercellular matrix, end up with further aggravates organ damage at same time[25].
How to reduce I-R injury has always been the focus and difficulty of medical research. Through evaluated oxidative stress biomarkers including SOD, MDA, GPx, myeloperoxidase (MPO), total antioxidant capacity (TAC) together with the indicator of liver, kidney, blood and lipid metabolism, El-Baset[26]、Pang[27]、Albadrani[28]、Zheng[7]、Soliman[29]、Mustafa[30] investigated the usage of Mesna, TGP, quercetin, parecobix, propolis and Tadalafi in repressing the I-R injury of lung, kidney, heart, intestine, cerebral nerve and liver respectively. Liu[31]has developed a kind of nanoparticle for antioxidant transportation to neutralize inflammatory factors, the material was proved to aliviate I-R induced acute kidney injury, providing a novel stradegy for I-R treatment.
Table 2. Application of oxidative stress biomarkers in I-R injury researches
|
Sample |
Intervention |
Rising indicator |
Dropping indicator |
Reference |
|
Rat lung |
Mesna |
SOD,GPx |
MPO |
[26] |
|
Rat kidney |
nanoparticle |
GSH,SOD |
MDA |
[31] |
|
Rat heart |
qurecetin |
SOD,GSH |
MDA,ROS |
[28] |
|
Rat intestine |
parecobix sodium |
TAC,SOD |
MDA,NO,MPO |
[7] |
|
Rat brain |
propolis |
GSH,CAT,SOD |
MDA |
[29] |
|
Rat liver |
Tadalafi |
GSH |
MDA,GSH |
[30] |
3. Reproductive system diseases research
① Idiopathic oligozoospermia
Idiopathic oligozoospermia (asthenospermia) is one of the most common factors of adult male infertility. The sperm density, survival rate and activity are significantly lower than the normal standard after excluding immune, infection, injury, chromosome abnormalities and other factors[32]. It has been proved that the concentration of nitrogen oxide in semen is negatively corelated with sperm activity, while the lower SOD level was obtained in idiopathic oligozoospermia patient[33] with the increasing of protein phosphorylation and DNA fragmentation.
Antioxidants, including vitamin C and vitamin E and others, having the ability of inhi



